All About Grease Types And Grades
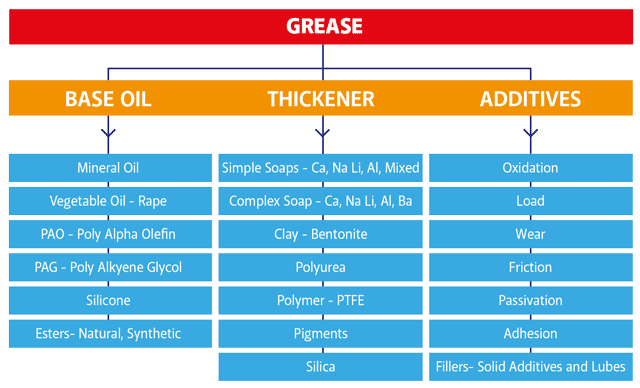
What is grease?
Grease is a semi-solid lubricant that is used to reduce friction between moving parts in machinery and equipment. It is composed of a base oil, a thickening agent, and additives that enhance its performance.
Why are grease types and grades important?
The types and grades of grease are important because they determine the suitability of the grease for a specific application. Different machinery and equipment require different types of grease to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
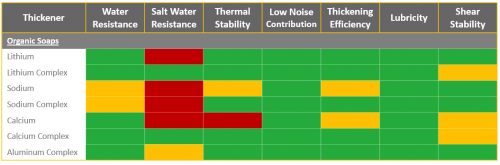
The type of grease refers to its composition and properties. There are several types of grease available, including lithium grease, calcium grease, and synthetic grease. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and they are suitable for different applications and operating conditions. For example, lithium grease is commonly used in automotive applications due to its high temperature stability and water resistance.
The grade of grease refers to its consistency or thickness. Grease grades are classified by the National Lubricating Grease Institute (NLGI) on a scale from 000 to 6, with higher numbers indicating thicker consistencies. The grade of grease required depends on factors such as the speed and load of the machinery, as well as the temperature and environment in which it operates. Using the wrong grade of grease can result in poor lubrication and potential damage to the equipment.
So, understanding grease types and grades is crucial for selecting the right lubricant for your machinery and equipment. It ensures smooth and efficient operation, reduces wear and tear, and extends the life of your equipment. Consult with a lubricant specialist or refer to equipment manufacturer recommendations to determine the most suitable grease type and grade for your specific application.

Lithium-based Greases
Lithium-based grease composition
Lithium-based greases are one of the most commonly used types of grease due to their excellent performance and versatility. These greases are formulated by combining lithium soap, which acts as the thickening agent, with a base oil and various additives. The base oil used can be mineral oil, synthetic oil, or a combination of both. The lithium soap thickener gives the grease its semi-solid consistency, allowing it to stay in place and provide long-lasting lubrication.
Advantages and applications of Lithium-based grease
Lithium-based greases offer numerous advantages that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. Firstly, they provide excellent mechanical stability, which means they can withstand high operating temperatures and heavy loads without losing their consistency or flow properties. This makes them ideal for use in automotive applications, industrial machinery, and equipment.
Additionally, lithium-based greases have good water resistance, which allows them to maintain their lubricating properties even in wet or humid conditions. This makes them suitable for outdoor applications or environments where water exposure is a concern.
The versatility of lithium-based greases extends to their compatibility with a wide range of seals and elastomers. They can be safely used with various rubber and plastic components without causing any degradation or damage.
Some common applications of lithium-based greases include automotive wheel bearings, chassis fittings, electric motor bearings, and general-purpose lubrication in industrial machinery. These greases provide reliable lubrication, protect against wear and corrosion, and extend the life of the equipment.
So, lithium-based greases are a popular choice due to their excellent performance, stability, and versatility. Their composition and properties make them suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive to industrial use. When selecting a lubricant, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of your equipment and consult with experts or refer to manufacturer recommendations to determine the most suitable lithium-based grease for your needs.
Calcium-based Greases
Calcium-based grease composition
Calcium-based greases are another commonly used type of grease due to their unique composition and advantageous properties. These greases are formulated by combining calcium soap, which acts as the thickening agent, with a base oil and various additives. The base oil used can be mineral oil, synthetic oil, or a blend of both. The calcium soap thickener gives the grease its semi-solid consistency, allowing it to stay in place and provide effective lubrication.
Advantages and applications of Calcium-based grease
Calcium-based greases offer several benefits that make them suitable for various applications. Firstly, they provide excellent water resistance, making them ideal for applications where exposure to water or moisture is a concern. This includes applications in marine environments, agricultural machinery, and off-road vehicles.
Additionally, calcium-based greases have good pumpability, which means they can flow easily through lubrication systems and reach critical components, ensuring proper lubrication. This characteristic makes them suitable for use in centralized lubrication systems and other machinery that requires efficient lubricant distribution.
Furthermore, calcium-based greases provide good anti-rust and anti-corrosion properties, protecting equipment and machinery from wear and damage caused by moisture and harsh environments. This makes them suitable for use in heavy-duty equipment, construction machinery, and mining applications.
Common applications of calcium-based greases include wheel bearings, chassis fittings, industrial machinery, and agricultural equipment. These greases provide reliable lubrication, protect against rust and corrosion, and extend the lifespan of the equipment.
So, calcium-based greases are widely used due to their unique composition and advantageous properties. Their water resistance, pumpability, and anti-corrosion characteristics make them suitable for a variety of applications, from marine and agricultural to industrial and construction use. When selecting a grease, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of your equipment and consult with experts or refer to manufacturer recommendations to determine the most suitable calcium-based grease for your needs.

Polyurea Greases
Polyurea greases are a type of synthetic grease that is widely used in various industries for their unique composition and advantageous properties. Here, we will explore the composition of polyurea greases and the advantages and applications they offer.
Polyurea grease composition
Polyurea greases are formulated by combining a polyurea thickener with a base oil and various additives. The polyurea thickener provides the grease with its unique characteristics, including extreme temperature resistance, high shear stability, and excellent mechanical stability. The base oil used in polyurea greases can be mineral oil, synthetic oil, or a blend of both. The specific combination of the thickener and base oil determines the performance and properties of the grease.
Advantages and applications of Polyurea grease
Polyurea greases offer several advantages that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. Firstly, they provide exceptional high-temperature stability, making them ideal for applications where extreme temperatures are encountered, such as in automotive engines, heavy machinery, and industrial equipment.
Additionally, polyurea greases have excellent mechanical stability, meaning they maintain their consistency and performance even under heavy loads and extreme pressures. This makes them suitable for use in applications that require reliable lubrication under demanding conditions, including bearings, gears, and sliding surfaces.
Furthermore, polyurea greases have excellent water resistance, ensuring effective lubrication even in wet or humid environments. This makes them suitable for marine applications, outdoor equipment, and machinery exposed to water or moisture.
Common applications of polyurea greases include automotive components, industrial machinery, bearings, and electric motors. Their high-temperature stability, mechanical stability, and water resistance make them a reliable choice for various industries.
So, polyurea greases offer unique advantages due to their composition and properties. Their high-temperature stability, mechanical stability, and water resistance make them suitable for a wide range of applications. When choosing a grease, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of your equipment and consult with experts or refer to manufacturer recommendations to determine the most suitable polyurea grease for your needs.
Aluminum Complex Greases
Aluminum Complex Grease Composition
Aluminum complex greases are a type of lubricating grease that is widely used in various industries for their unique composition and advantageous properties. These greases are formulated by combining an aluminum complex soap thickener with a base oil and additives. The aluminum complex soap thickener provides the grease with its unique characteristics, including excellent mechanical stability, high temperature resistance, and water resistance. The base oil used in aluminum complex greases can be mineral oil, synthetic oil, or a combination of both. The specific combination of the thickener and base oil determines the performance and properties of the grease.
Advantages and Applications of Aluminum Complex Grease
Aluminum complex greases offer several advantages that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. Firstly, they have excellent mechanical stability, meaning they can withstand heavy loads and extreme pressures without losing their consistency or lubrication effectiveness. This makes them an ideal choice for applications such as bearings, gears, and sliding surfaces.
Additionally, aluminum complex greases offer high-temperature resistance, allowing them to perform well under extreme heat conditions. This makes them suitable for use in automotive applications, industrial machinery, and other equipment that generates high levels of heat.
Furthermore, Aluminum complex greases have excellent water resistance, making them highly effective in wet or humid environments. They can provide reliable lubrication even in the presence of water or moisture. This makes them suitable for marine applications, outdoor equipment, and machinery that is exposed to water or other liquids.
Common applications of aluminum complex greases include automotive components, industrial machinery, construction equipment, and electric motors. Their excellent mechanical stability, high-temperature resistance, and water resistance make them a reliable choice in various industries.
So, aluminum complex greases offer unique advantages due to their composition and properties. Their excellent mechanical stability, high-temperature resistance, and water resistance make them suitable for a wide range of applications. When selecting a grease, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of your equipment and consult with experts or refer to manufacturer recommendations to determine the most suitable aluminum complex grease for your needs.

Synthetic Greases
Composition and Advantages of Synthetic Greases
Synthetic greases are a type of lubricating grease that are formulated using synthetic base oils, as opposed to mineral oils. These greases are known for their superior performance and properties compared to conventional greases. They offer several advantages due to their unique composition.
Synthetic greases are formulated using a combination of synthetic base oils, such as polyalphaolefin (PAO), polyalkylene glycol (PAG), or ester-based oils, along with special additives. These additives enhance the performance of the grease by providing properties like extreme pressure resistance, anti-wear protection, and corrosion resistance.
One of the key advantages of synthetic greases is their wide temperature range capability. They can maintain their consistency and provide effective lubrication at both high and low temperatures. This makes them suitable for applications that experience extreme temperature conditions, such as automotive engines, industrial machinery, and aerospace equipment.
Additionally, synthetic greases have excellent oxidation stability. They resist degradation and maintain their performance over extended periods, even under high temperatures and in the presence of oxygen. This results in longer grease life and reduced maintenance requirements.
Synthetic greases also offer superior resistance to water and moisture. They can maintain their lubrication properties even in wet or humid environments, making them suitable for marine applications, water treatment plants, and outdoor equipment.
Common Synthetic Grease Types
There are several types of synthetic greases available in the market, each with its own unique properties and applications. Some of the common types include:
- Polyurea Grease: These greases are formulated using a polyurea thickener and provide excellent mechanical stability and high-temperature performance. They are commonly used in electric motors, automotive bearings, and other applications requiring long-lasting lubrication.
- Silica Grease: These greases use a silica thickener and provide excellent high-temperature performance, along with good resistance to oxidation and corrosion. They are commonly used in high-temperature applications such as oven conveyors and kiln bearings.
- PTFE Grease: These greases contain polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) particles, which provide excellent lubricity and reduce friction. They are commonly used in applications with sliding surfaces, such as door hinges, drawer slides, and bicycle chains.
- Bentone Grease: These greases use a bentonite clay thickener and offer excellent mechanical stability and water resistance. They are commonly used in marine applications, as well as in environments with high levels of water contamination.
So, synthetic greases offer numerous advantages due to their unique composition and properties. They provide superior temperature range capability, oxidation stability, and water resistance. There are various types of synthetic greases available to cater to different applications and requirements. When choosing a synthetic grease, it is important to consider the specific needs of your equipment and consult with experts for the most suitable option.

NLGI and ASTM Grease Grades
What are NLGI and ASTM grease grades?
NLGI stands for the National Lubricating Grease Institute, while ASTM refers to the American Society for Testing and Materials. Both NLGI and ASTM have established standards for classifying and grading greases based on their consistency and performance properties. These standards help users determine the most suitable grease for their specific application.
NLGI grease grades are based on the stiffness of the grease, ranging from 000 (fluid) to 6 (very stiff). This grading system provides an indication of the grease’s hardness or softness, which in turn affects its flow properties and ability to provide lubrication. Greases with lower NLGI grades are more fluid and suitable for applications that require easy flow and penetration, such as open gears. On the other hand, greases with higher NLGI grades are more solid and suitable for applications that require longer life and better sealing, such as wheel bearings.
ASTM grease grades, on the other hand, are designated by a series of letters, such as AA, BB, or EP. These grades indicate the specific requirements and performance characteristics of the grease. For instance, EP stands for extreme pressure additive, indicating that the grease is suitable for applications that experience heavy loads and high pressures.
Understanding the significance of grease grades
NLGI and ASTM grease grades are crucial for selecting the right grease for each application. By understanding the significance of these grease grades, users can ensure proper lubrication and enhance equipment performance. Choosing the wrong grease grade can result in inadequate lubrication, leading to premature wear, increased friction, and potential equipment failure.
Grease grades help users identify the most suitable grease for specific applications based on factors such as operating temperature, load-bearing capacity, and speed. For example, applications with high temperatures or heavy loads may require a higher NLGI grade grease to withstand the conditions and provide effective lubrication.
Additionally, grease grades ensure consistency and uniformity across the industry. They provide a common language and standard for manufacturers, distributors, and end-users to communicate and understand the properties and limitations of different greases. This helps to ensure that the right grease is selected and used consistently, minimizing the risk of compatibility issues or performance discrepancies.
So, NLGI and ASTM grease grades play a significant role in the proper selection and application of greases. Understanding these grades allows users to choose the most suitable grease for their specific needs, ensuring proper lubrication, equipment performance, and extended service life.
Choosing the Right Grease Type and Grade
Factors to consider when selecting grease
When it comes to choosing the right grease for your application, there are several factors that need to be considered. These factors will help you determine the most suitable grease type and grade for optimal performance and longevity.
- Operating Temperature: The temperature at which your equipment operates is a crucial factor to consider. Greases have different temperature limits, and choosing the appropriate grease with the right temperature range ensures that it maintains its consistency and lubricating properties.
- Load-Bearing Capacity: The load-bearing capacity of the grease is another important consideration. If your application involves heavy loads, you will need a grease with high load-carrying capabilities to prevent metal-to-metal contact and excessive wear.
- Speed: The speed at which your equipment operates will also impact the choice of grease. High-speed applications require a grease that can withstand shear forces and maintain its lubricating properties under these conditions.
- Environmental Factors: Consider any environmental factors that may impact the performance of the grease, such as exposure to water, chemicals, dirt, or extreme weather conditions. Some greases are formulated to resist these elements better than others.
Matching grease type and grade to application requirements
Once you have considered the factors mentioned above, you can choose the appropriate grease type and grade for your application. Different applications require different grease types and grades to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Thickener type is an important consideration when selecting grease. Common types include lithium, calcium, aluminum, and polyurea. Each thickener type has its own unique properties and advantages, such as better resistance to water or high-temperature conditions.
NLGI and ASTM grease grades are helpful guides to determine the right grease consistency and performance characteristics. NLGI grades provide an indication of the grease’s stiffness, ranging from 000 (fluid) to 6 (very stiff). ASTM grades, on the other hand, specify the grease’s specific requirements and performance characteristics.
It is essential to consult the equipment manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines when selecting the right grease type and grade. They often provide specific information on the grease requirements for optimal performance and warranty compliance.
So, by considering factors such as operating temperature, load-bearing capacity, speed, and environmental factors, and by matching the grease type and grade to application requirements, you can choose the right grease that will ensure proper lubrication, equipment performance, and extended service life.
So, In short, Grease is a semi-solid lubricant that is typically made by combining a base oil with a thickening agent. Various types and grades of grease are available to suit different applications and operating conditions. The National Lubricating Grease Institute (NLGI) has established a classification system that defines grease based on its consistency. The NLGI consistency grades range from 000 (very soft) to 6 (very hard). Here’s a basic overview of grease types and grades:
- NLGI Consistency Grades:
- NLGI 000, 00, 0: Very soft greases, often used in centralized lubrication systems or in applications requiring a very low-viscosity grease.
- NLGI 1, 2: General-purpose greases used in a wide range of applications. NLGI 2 is the most common grade for general-purpose lubrication.
- NLGI 3: Semi-fluid greases, suitable for low-speed or high-temperature applications.
- NLGI 4, 5, 6: Hard greases used in applications where a more solid lubricant is required, such as open gears or heavily loaded bearings.
- Thickener Types:
- Lithium Grease: Commonly used for general-purpose applications. It has good temperature and water resistance.
- Calcium Grease: Offers good water resistance but has a lower temperature tolerance compared to lithium grease.
- Polyurea Grease: Known for its high-temperature stability and excellent shear stability.
- Aluminum Complex Grease: Provides good water resistance and is often used in food-grade applications.
- Sodium Grease: Used in high-temperature applications but has poor water resistance.
- Specialized Greases:
- High-Temperature Grease: Formulated to withstand elevated temperatures without breaking down.
- Low-Temperature Grease: Maintains its lubricating properties at very low temperatures.
- High-Load Grease: Designed for applications with heavy loads or extreme pressure conditions.
- Biodegradable Grease: Environmentally friendly and designed to break down over time.
- Application-Specific Greases:
- Automotive Grease: Formulated for use in automotive applications, such as wheel bearings.
- Marine Grease: Resistant to water and corrosion, suitable for marine applications.
- Food-Grade Grease: Used in the food and beverage industry, where incidental contact with food is possible.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines for the specific grease to be used in a particular application. The choice of grease depends on factors such as temperature, load, speed, and environmental conditions.
Conclusion
So, choosing the right grease type and grade is crucial to ensure proper lubrication, equipment performance, and extended service life. By considering factors such as operating temperature, load-bearing capacity, speed, and environmental factors, and matching the grease type and grade to application requirements, you can make an informed decision.
Summary of Grease Types and Grades
When selecting a grease type, it is important to consider the thickener type. Common types include lithium, calcium, aluminum, and polyurea, each with its own unique properties and advantages. Some greases are formulated to resist water or high-temperature conditions better.
NLGI and ASTM grease grades provide valuable information regarding grease consistency and performance characteristics. NLGI grades indicate the grease’s stiffness, ranging from 000 (fluid) to 6 (very stiff), while ASTM grades specify the grease’s specific requirements and performance characteristics.
Tips for Proper Grease Selection and Maintenance
To ensure optimal grease selection and maintenance, it is recommended to consult the equipment manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines. They often provide specific information on the grease requirements for optimal performance and warranty compliance.
Regular inspection and lubrication maintenance schedules should be followed to ensure the grease continues to perform effectively. Additionally, it is essential to monitor the equipment’s performance and conditions to detect any signs of excessive wear or grease breakdown.
Proper storage and handling of grease are also important to maintain its quality. Keep grease containers tightly sealed and store them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures.
By following these tips and guidelines, you can ensure that the right grease type and grade are chosen for your specific application and that proper maintenance practices are followed to maximize equipment performance and longevity.







