Tool Comparison: Budget Vs Professional for Diagnosing Faulty Diagnostic Steps
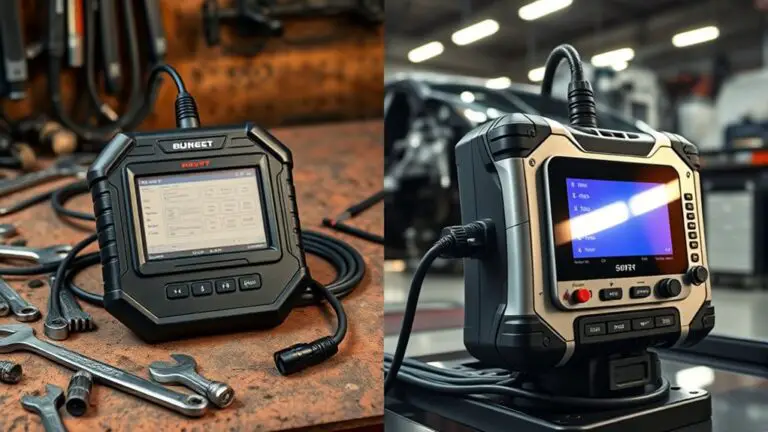
When you compare budget versus professional tools for diagnosing faulty diagnostic steps, you weigh speed and cost against accuracy and depth. Budget tools give fast, low-cost checks for routine symptoms, but may miss subtle faults. Professional tools provide deeper data, higher reliability, and robust support, especially in high-stakes cases. Consider data fidelity, latency, and maintenance…