DIY: Repairing Corroded Grounds Safely
To repair corroded electrical grounds safely, verify power is off by confirming with a voltage tester. Inspect and clean corroded connections using wire brushes or sandpaper until shiny. Apply a corrosion inhibitor for lasting protection before reestablishing secure connections. Always wear protective gear and maintain a safe work environment to prevent hazards. Regular inspections can help identify issues early. You’ll discover further effective strategies to maintain your electrical system and prevent future corrosion.
Understanding Corrosion and Its Impact on Electrical Systems

When you consider the integrity of electrical systems, it is crucial to understand how corrosion can compromise their functionality. Corrosion causes, such as moisture, contaminants, and electrochemical reactions, lead to the deterioration of conductive materials. This degradation can create resistance in electrical connections, resulting in electrical failures that disrupt the flow of current. Inadequate grounding due to corroded components can heighten the risk of shock hazards and equipment malfunctions.
Additionally, corrosion often goes unnoticed until it manifests as a significant issue, making regular inspections critical. Understanding the implications of corrosion empowers you to take proactive measures to mitigate potential risks. By maintaining vigilance over electrical systems and addressing corrosion promptly, you can preserve their reliability and safety. Ultimately, grasping the mechanics of corrosion allows you to maintain autonomy over your electrical environment, ensuring it remains functional and secure.
Identifying Corroded Grounds in Your Home
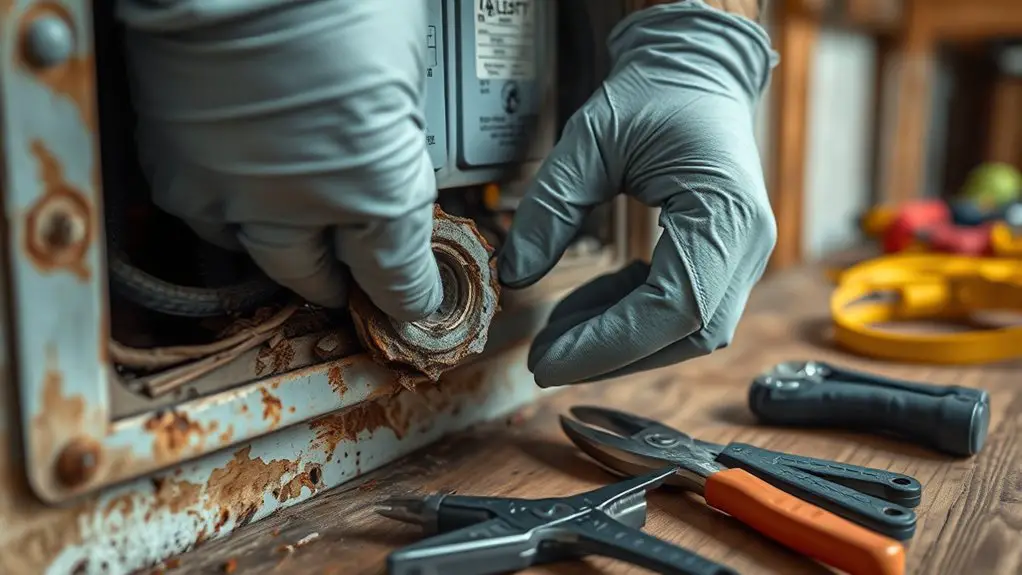

How can you effectively identify corroded grounds in your home? Start by inspecting your electrical outlets and panels. Look for signs of corrosion, such as discoloration, rust, or white powdery residues around connection points. These can indicate grounding issues that may compromise safety and performance. Next, check the grounding rods outside, ensuring they’re firmly connected and free from corrosion. If you notice any exposed wires, they’re also vulnerable to corrosion, so take note.
You should also assess devices that frequently trip circuit breakers, as these might be symptomatic of underlying grounding problems. Finally, don’t overlook the importance of testing your circuit with a multimeter to verify proper grounding functionality. By systematically examining these areas, you can pinpoint corroded grounds and address potential electrical hazards before they escalate.
Safety Precautions Before Starting Repairs
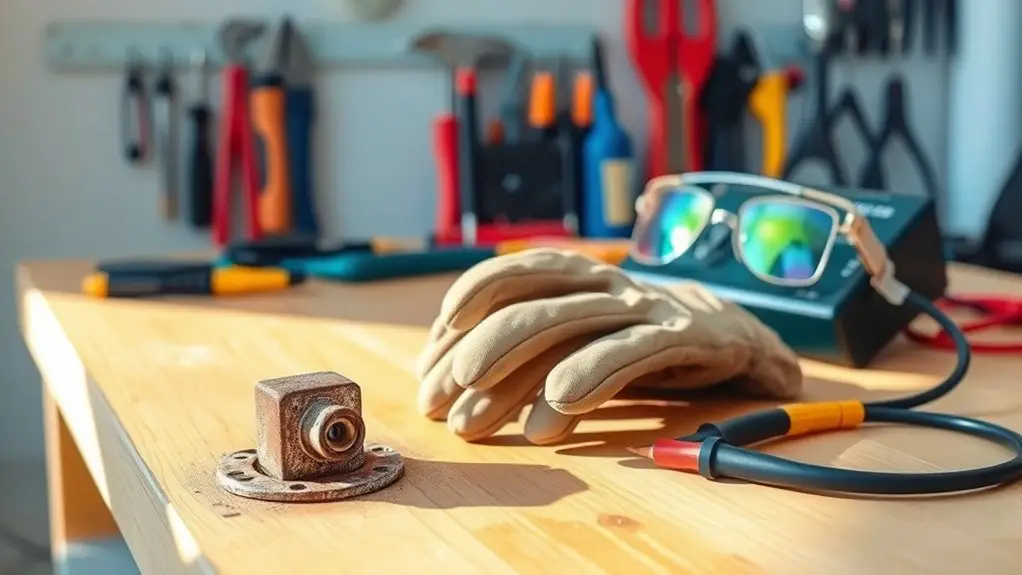

Before initiating any repairs on corroded grounds, it’s essential to affirm you’ve taken the necessary safety precautions. Start by verifying you’re equipped with appropriate protective gear, such as gloves, goggles, and insulated footwear. This minimizes the risk of injury and exposure to harmful substances. Electrical safety is paramount; always turn off the power to the affected area and use a voltage tester to confirm that it’s safe to proceed.
Here’s a quick reference table for your safety precautions:
| Safety Measure | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Protective Gear | Use gloves, goggles, and boots. | Prevents injuries and exposure. |
| Power Shutoff | Turn off electricity before repairs. | Reduces electrical hazards. |
| Voltage Testing | Confirm no live wires are present. | Affirms safe working conditions. |
Tools and Materials Needed for Repairing Corroded Grounds
To effectively repair corroded grounds, you’ll need a specific set of tools and materials that guarantee a successful outcome. Essential tools include wire brushes, multimeters, and wrenches, while necessary materials typically consist of corrosion inhibitors and replacement connectors. Understanding these components is vital for a thorough and efficient repair process.
Essential Tools Overview
Repairing corroded grounds requires a specific set of tools and materials to guarantee effective restoration and long-lasting results. You’ll need a multimeter for electrical safety checks, ensuring no live currents are present before you start your work. Wire brushes and sandpaper are essential for cleaning corroded surfaces, while heat-shrink tubing provides corrosion prevention by sealing connections effectively. A soldering iron is vital for repairing damaged wires, ensuring a strong electrical bond. Finally, a reliable set of pliers and wrenches will help you manipulate and tighten connections securely. By equipping yourself with these tools, you’ll be prepared to tackle corrosion with confidence, enhancing the longevity of your electrical systems and ensuring overall safety.
Necessary Materials Explained
When tackling corroded grounds, understanding the necessary materials is fundamental for achieving a successful repair. You’ll need a wire brush or sandpaper for cleaning corroded areas, guaranteeing a solid base for grounding techniques. Copper wire or conductive metal connectors are essential for establishing reliable connections.
Corrosion prevention materials, like anti-corrosive spray or electrical grease, help protect your repairs from future deterioration. Insulation tape or heat shrink tubing guarantees that exposed wire connections remain secure and safe from moisture. Finally, a multimeter is critical for testing electrical continuity and verifying that your grounding setup is effective. With these tools and materials, you can confidently tackle corrosion issues and maintain a reliable electrical system.
Step-by-Step Guide to Repairing Corroded Grounds
Corroded grounds can greatly impact electrical systems, leading to inefficiencies or failures. To repair them, first, verify power is off at the main breaker. Identify the corroded area and remove any insulation or coverings. Use a wire brush or sandpaper to clean the corroded connections until you reach shiny metal. Apply a corrosion inhibitor to prevent future issues.
Next, re-establish the connection using proper grounding techniques. If the wire is excessively damaged, replace it with a new grounding wire of equal or greater gauge. Secure connections tightly to guarantee conductivity and minimize resistance. Finally, cover the repaired area with appropriate insulation to protect it from moisture and other environmental factors.
Maintaining Your Electrical System to Prevent Future Corrosion
To guarantee the longevity of your electrical system and minimize the risk of future corrosion, it’s essential to implement regular maintenance practices. Preventive maintenance and regular inspections can considerably enhance your system’s resilience against corrosion. Here’s a concise overview to guide you:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | Identify visible issues |
| Cleaning Connections | Quarterly | Remove dirt and debris |
| Tightening Fasteners | Biannually | Confirm secure connections |
| Testing Grounding | Annually | Verify effective grounding |
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can I Tell if Corrosion Is Affecting My Appliances?
You can tell if corrosion’s affecting your appliances by inspecting for visible signs like rust or discoloration around the connections. Use corrosion detection methods such as a voltmeter to check for irregular voltage readings, which may indicate issues. Regular appliance maintenance is essential; if you notice any unusual smells, sounds, or diminished performance, it’s time to investigate further. Ignoring these signs could lead to more serious damage or safety hazards down the line.
What Are the Signs of Electrical System Failure Due to Corrosion?
You’ll notice several corrosion indicators when your electrical system’s failing. Look for electrical symptoms like flickering lights, frequent circuit breaker trips, or inconsistent power delivery. You might also see visible corrosion on terminals or connectors, which can lead to poor conductivity. If devices are underperforming or heating excessively, that’s another red flag. Regular inspections can help you catch these issues early, ensuring your electrical system remains safe and effective.
Can I Use Household Cleaners on Corroded Grounds?
You shouldn’t use household cleaners on corroded grounds. While they seem convenient, many contain chemicals that can further damage electrical components or create safety hazards. Instead, focus on corrosion cleaning methods specifically designed for electrical systems, like vinegar or baking soda. Always prioritize household cleaner safety; make certain you’re using products that won’t react negatively with metals. Properly cleaning these areas requires care to prevent additional corrosion and maintain system integrity.
Is Professional Help Necessary for Severe Corrosion Issues?
You might think tackling severe corrosion issues yourself is a grand adventure, but it’s often a recipe for trouble. Depending on the corrosion types—like galvanic or pitting—repair techniques vary in complexity and risk. Professional help isn’t just advisable; it’s often necessary to guarantee safety and effectiveness. They’ve got the expertise to assess damage and implement the right solutions, freeing you from the stress of potential mishaps and guaranteeing long-term stability.
How Often Should I Inspect My Electrical Grounds for Corrosion?
You should inspect your electrical grounds for corrosion at least once a year as part of a regular ground maintenance routine. If you live in a humid or corrosive environment, consider increasing your inspection schedule to every six months. Regular inspections help identify early signs of corrosion, ensuring your system remains efficient and safe. Keeping a detailed log of your findings can also aid in managing potential issues before they escalate.