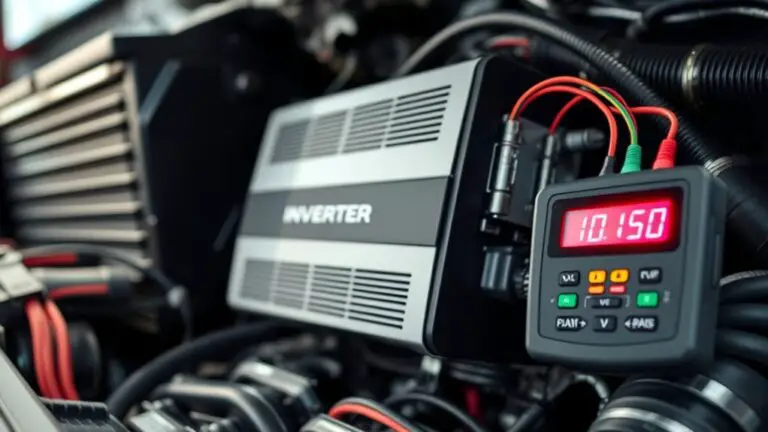
Charging Tips to Avoid Inverter Fault and Extend Battery Life
To avoid inverter faults and extend battery life, match your charger output to your battery type (lead-acid, gel/AGM, or lithium) and use proper charging stages (bulk, absorption, float) with safeguards like current limits and temperature compensation. Manage depth of discharge by staying within low DoD to reduce stress, and avoid deep cycles. Control temperature during…