Cost Guide: Repairing a Radiator Cap Failure Vs Replacing Major Fan Relay
A radiator cap failure is inexpensive to fix with a simple replace-and-seal approach, typically under an hour for labor and low-cost parts, with minimal downtime. Replacing a major fan relay is pricier: parts can be more complex, and diagnostic time plus labor may extend to one or two hours, plus potential hidden fees for inspection or surcharges. You’ll save on cap costs but may face higher total for the relay, depending on diagnostics—and there’s more to learn below.
Understanding the Problem: Radiator Cap Failure Vs Major Fan Relay
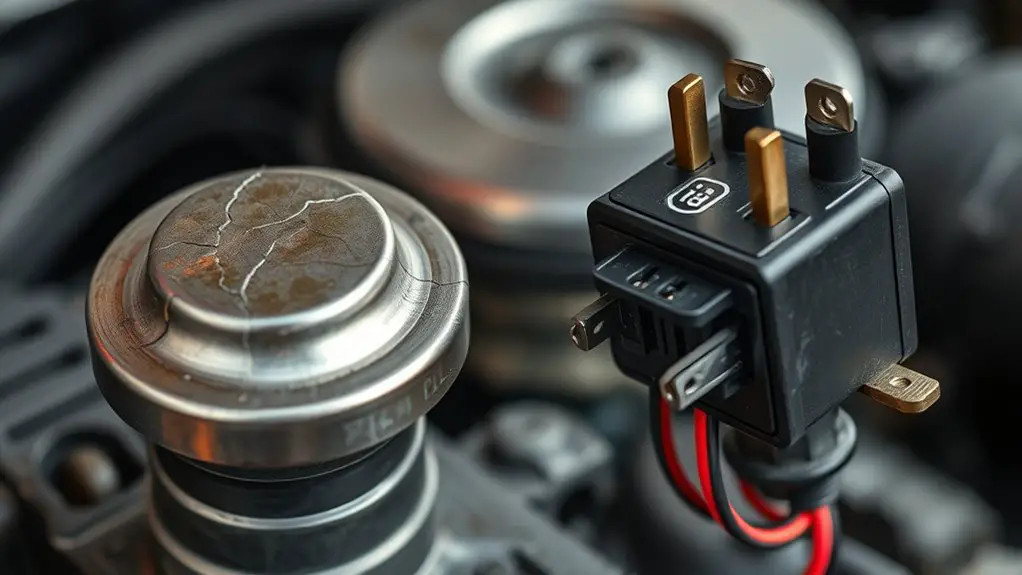

A radiator cap failure and a major fan relay issue can produce very different symptoms and failure modes, so distinguishing between them is key. You’ll notice pressure anomalies with a faulty radiator cap: coolant boils at a lower temperature, cap seals fail, and you may see overflow. Inconsistent pressure can lead to loss of coolant and steam, triggering warning lights without obvious electrical symptoms. By contrast, a failed fan relay typically causes intermittent or persistent cooling fan operation issues, affecting engine temperature stability, idle quality, and HVAC performance. You’ll hear or feel the fan click or stay off when the engine heats up, and temperature spikes can occur without coolant loss. Testing approaches differ: pressure tests and cap inspection for radiator cap, electrical continuity and relay coil/contacts for fan relay. Prioritize safe diagnosis, isolate the circuit, and verify both components in the correct operating window to prevent misdiagnosis and cascading damage. radiator cap, fan relay.
Cost Breakdown: Parts, Labor, and Hidden Fees for Each Repair
When you compare repairs for radiator cap replacement versus a fan relay fix, cost components differ in predictable ways. You’ll see parts costs lean higher for a relay than a cap, due to a complex switch, wiring, and mounting hardware. A radiator cap is simple, inexpensive, and often single-use, with minimal stocking impact. Labor time for a cap swap is short, typically under an hour, reducing shop rates exposure. Relay repairs demand more diagnostic time, testing, and possible system rechecks, pushing labor toward the next hour or two. Hidden fees vary: inspection fees may apply to both, but relay work can incur diagnostic surcharges if the issue isn’t immediately visible, and core charges for replaced components may appear. In a clean cost comparison, plan for higher upfront parts and potentially longer labor for the relay, while recognizing budget-friendly, straightforward pricing for a radiator cap. Your best repair options balance certainty, downtime, and total cost.
Timeline and Repair Steps: What to Expect From Diagnosis to Fix
Diagnosing and fixing radiator-cap versus fan-relay issues follows a structured sequence: initial symptom verification, targeted diagnostics, component testing, and a confirmed repair plan. You’ll move through the diagnostic process with deliberate steps, documenting findings and aligning expectations with the repair timeline.
1) Observe symptoms, confirm vehicle conditions, and note any related indicators (temperature gauge, warning lights).
2) Perform targeted diagnostics, including live data review and system-specific tests to isolate the fault.
3) Execute component testing and implement a data-driven repair plan, then verify functionality after completion.
In this timeline, you’ll confirm reported symptoms, identify root causes, and validate fixes with functional checks. The diagnostic process emphasizes measurable results and reproducible tests, while the repair timeline outlines sequential actions, parts availability, and estimated downtime. By staying precise and disciplined, you minimize back-and-forth, clarify scope, and guarantee a reliable repair outcome without unnecessary delays. Plan for rechecks after road testing to confirm sustained operation and to guard against reoccurrence.
Risk Assessment: Potential Follow-Up Issues and Long-Term Reliability
After addressing the immediate diagnostic findings and completing the repair plan, you’ll want to contemplate how follow-up issues could surface and what long-term reliability looks like for radiator cap and fan relay repairs. In practice, consider potential wear-induced failures, seal degradation, and thermostat or cooling system interactions that could reappear under heat cycling or temperature spikes. Long term implications include gradual loss of pressure integrity, intermittent cooling performance, and sporadic cooling fan operation that may stress the water pump or hoses. Reliability factors hinge on material compatibility, proper torque, and correct electrical connections; mismatches can accelerate corrosion, arcing, or contact wear. You should monitor for warning indicators like rising coolant temperature, gauge fluctuations, or cooling fan delays. Plan for environmental exposure, vibration, and electrical noise that can influence connector integrity. While repairs address present faults, persistent operating conditions will determine enduring success and the likelihood of requiring future maintenance or part replacements.
Practical Guidance: When to DIY, When to Seek a Pro, and Preventive Tips
Practical guidance starts with evaluating your own capabilities and the task’s complexity: DIY is often suitable for straightforward radiator cap or fan relay issues, while ambiguous symptoms, safety concerns, or compromised wiring call for a pro. You’ll balance time, cost, and risk, then decide whether to pursue DIY considerations or seek Professional advice.
1) DIY considerations: confirm tool access, test procedures, and replacement parts; follow manufacturer specs; stop if symptoms worsen.
2) When to seek a pro: uncertain diagnostics, overheating signs, coolant leaks, or electrical fault indicators require professional assessment.
3) Preventive tips: routine inspections, clutching heat-stress cycles, and keeping electrical connections clean reduce failure chances and extend system life.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Radiator Cap Failures Affect Engine Cooling Efficiency Over Time?
A surprising 15% of engine overheating events trace to loose or failed radiator caps. You’ll see cooling system efficiency drop as pressure loss increases, causing lower boiling points and reduced coolant flow over time. When the cap fails, you lose maintained system pressure, so your engine runs hotter, especially under load. You’ll notice gradual temperature rise, more fan cycling, and reduced heat transfer, compromising performance and longevity. Fix promptly to restore proper cooling and reliability.
Can a Faulty Fan Relay Cause Intermittent Overheating Without Leaks?
Yes, a faulty fan relay can cause intermittent overheating without leaks. When the relay sticks or fails to energize, the cooling fan may not run at needed speeds, triggering overheating causes even though there’s no coolant loss. Look for fan relay symptoms like delays in fan engagement, buzzing sounds, or inconsistent cooling. If you notice these signs, test or replace the relay promptly to prevent engine damage and preserve your freedom to drive.
Are There Common Hidden Damage Signs After Replacing a Radiator Cap?
Hidden leaks are your clue—after replacing a radiator cap, inspect for any seepage around hoses, clamps, and the radiator neck. Perform pressure tests to verify the system holds, and watch for slow drips during the test. Look for lingering condensation or damp spots under the cap area. If the pressure bleeds off quickly, investigate the cap seating, radiator core, and coolant reservoir for hidden damage or improper reseating.
Will Replacing a Fan Relay Impact Fuel Economy or Emissions?
Replacing a fan relay can affect fan operation, but it doesn’t inherently alter fuel economy or emissions noticeably. If the relay restores proper cooling, you may see steadier engine temperatures, which helps maintain ideal efficiency. The key is to verify the replacement is correct for your vehicle and wired properly. fan relay impacts are most noticeable in cooling reliability; fuel economy benefits come from avoiding overheating and preventing compensating engine behaviors.
How Long Can a System Run Safely With a Degraded Radiator Cap?
A quick truth: you shouldn’t run with a degraded radiator cap for long. You can safely operate for only a short period, but engine overheating risks rise quickly as coolant pressure drops. Expect the radiator cap lifespan to shorten if you ignore it. If you notice rising temps or steam, stop and inspect. Stay aware of cooling system integrity, because neglect can trigger rapid overheating and serious engine damage.







