How to Diagnose BMS Warning in a Battery EV Powertrain
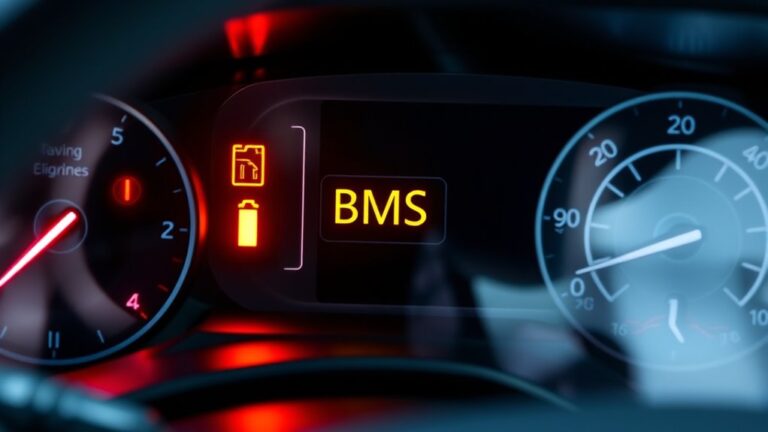
To diagnose a BMS warning in an EV powertrain, start with safety and isolate the system, then collect fault codes and live data. Verify cell voltages, SOC/SOH, and pack health against specs. Check cooling system performance, coolant temps, and flow, plus sensor accuracy. Inspect CAN/PCM communication, physical layers, and error frames. Form hypotheses per subsystem—cell…