Preventive Maintenance to Avoid Airbag Connector Corrosion With Airbags and ABS
To prevent airbag and ABS connector corrosion, you should establish a standards-driven maintenance routine that emphasizes clean, dry contacts and secure mating. Inspect for signs of moisture ingress, pitting, or coating degradation, and document findings with dates, locations, and photos. Use dedicated tools, anti-static measures, and approved cleaners, then reseat connectors and reseal as specified. Schedule regular maintenance, replace damaged seals, and maintain traceable logs to prove integrity; soon you’ll master proactive safeguards and safer deployments.
Understanding the Risks of Airbag and ABS Connector Corrosion

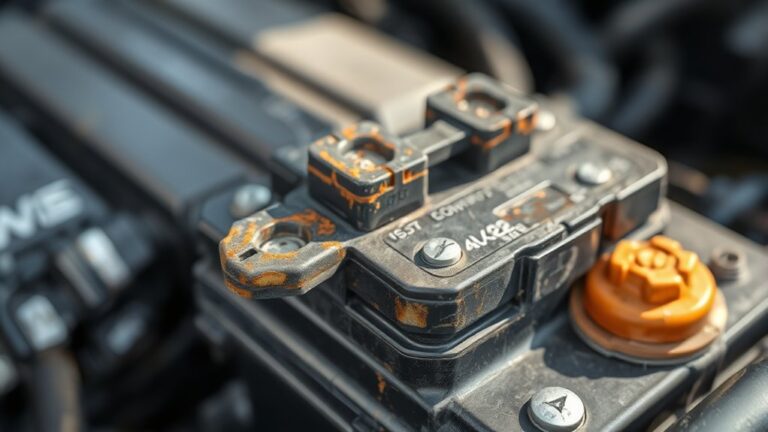
Corrosion at airbag and ABS connectors poses a clear safety risk by degrading electrical continuity and signal integrity. You’ll inspect the risk factors with a systematic mindset, focusing on connection surfaces, contact pressure, and material compatibility. Corrosion can form at pins, housings, or seals where moisture, salt, or contaminants reside, compromising sensor data and deployment timing. You should quantify exposure by loggable events, such as splash, humidity, or road salt exposure, and correlate them with service intervals. Implement strict cleanliness during maintenance, using approved contact cleaners and lint-free wipes, ensuring no residue remains that could attract moisture. Establish a baseline for connector integrity with torque specifications and inspection criteria, documenting any deviations. Prioritize airbag safety through proactive corrosion prevention measures, including protective coatings, proper sealing, and timely replacement of aging connectors. Your discipline in these steps supports reliable system performance and freedom to trust your vehicle’s safety functions.
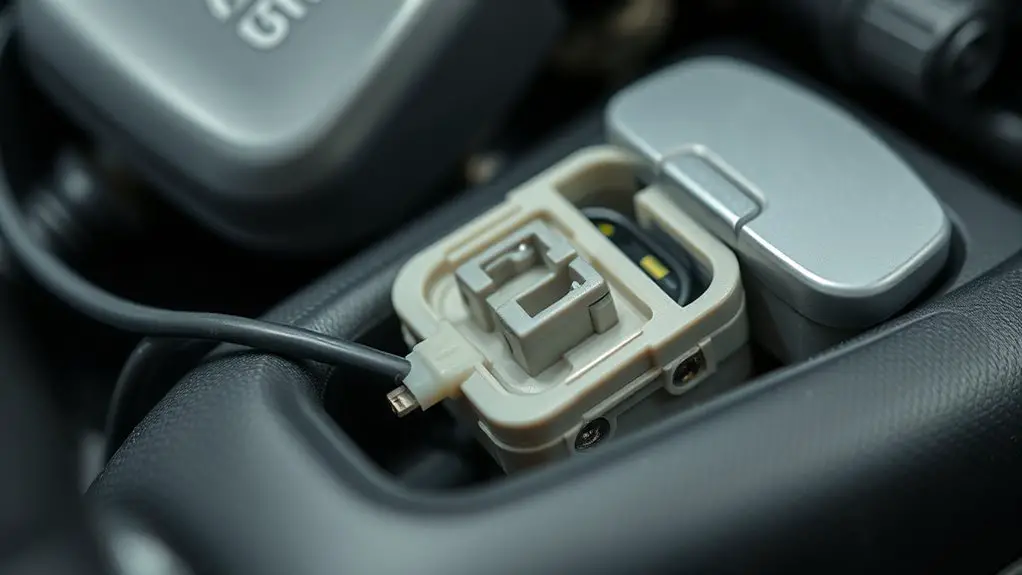
Signs of Corrosion and Moisture Ingress to Watch For
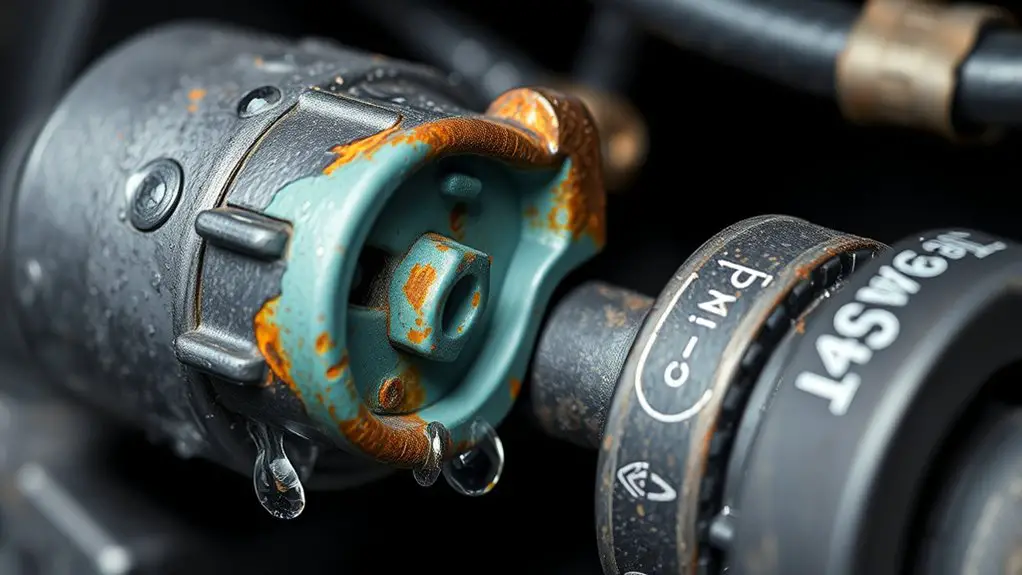

Even with proper protection in place, you should routinely inspect for telltale signs of moisture intrusion and corrosive effects, because early indicators can avert sudden airbag or ABS failures. You’ll look for corrosion indicators on connectors, pins, and housings—pitting, discoloration, roughness, or white powder on metal surfaces. Moisture sources may appear as condensation streaks, damp seals, or evidence of exposure to splash and humidity, especially at weather seals and connector joints. Check for coating degradation, green or blue verdigris where copper alloys are present, and any loosening of locking mechanisms or mismatch of mating surfaces. You should test for corrosion progress by measuring pin play and absence of continuity with a calibrated meter, noting any increased resistance. Document suspicious areas with date, location, and visible condition. Prioritize areas near brake and airbag modules, harness junctions, and ABS control circuits. Maintain a disciplined visual log to support preventive timelines and safe, reliable function.
Tools and Safety Precautions for Inspection and Cleaning

To inspect and clean airbags and related components safely, you’ll work with purpose-built tools and follow strict safety protocols. Your approach is precise and systematic: verify battery status and disable airbag circuits before any contact, then inspect surfaces for corrosion indicators. Use dedicated inspection tools to measure connector cleanliness, verify pin integrity, and confirm wiring harness routing complies with manufacturer guidelines. Maintain a clean, organized workspace to prevent debris ingress and accidental misconnection. When handling connectors, wear anti-static gloves and safety glasses; avoid forcing fittings and never pry with metal tools. Document findings with clear notes and photos for traceability. For cleaning, select compatible cleaning solutions specified by the OEM, and apply sparingly to avoid liquid intrusion into sealed modules. Keep solvents away from exposed electronics and elastomeric seals. After work, reassemble only when components are dry and connections are secure, then restore electrical power and perform a post-inspection check.
Step-by-Step Cleaning Procedures for Connectors
Begin with a clear, methodical rinse of the connector surfaces, then apply a manufacturer-approved cleaner to the contact area only. You proceed in strict, repeatable steps to avoid damage or residue. Inspect the connector pins, looking for corrosion, pitting, or loose terminals, and document findings as required. Use minimal moisture; keep solvents off plastic housings unless specified in the cleaner’s guidelines. Apply cleaner with a lint-free pad or swab, wiping along the connector face from edge to edge, never scrubbing across pins. Allow a brief air-dry interval, verifying complete evaporation before reassembly. Recheck mating surfaces for uniform cleanliness and intact alignment features. If you encounter stubborn residue, repeat the gentle cleaning cycle, then dry thoroughly. Record the completed procedure, including materials used and any anomalies. This approach emphasizes cleaning techniques that preserve connector materials while maintaining system reliability and readiness for reinstallation, without introducing unnecessary fluids or abrasive actions.
Protective Measures to Prevent Future Corrosion
Protective measures to prevent future corrosion begin with creating an environment that minimizes moisture exposure and promotes clean, dry connections. You should implement controlled humidity levels in maintenance areas and store components in sealed, desiccated containers to reduce ambient moisture uptake. Use torque specifications and locking mechanisms that maintain consistent clamping force, preventing micro-movements that invite moisture ingress. Apply dielectric, non-conductive coatings only as specified, ensuring complete coverage without bridging contacts. Prioritize corrosion-resistant fasteners and seals rated for automotive environments, replacing degraded parts promptly. Establish a routine inspection protocol focusing on connector housings, pins, and sleeves for signs of oxidation, pin wear, or seal compromise. Incorporate preventive measures such as timely replacement schedules and traceability of material batches. Consider corrosion inhibitors where approved by the original equipment manufacturer, applying in accordance with product data sheets. Maintain documentation to support lifecycle decisions while enabling a transparent, freedom-respecting maintenance culture.
Recommended Maintenance Intervals and Documentation
Having established corrosion-resistant measures, you’ll define clear maintenance intervals and keep thorough records to sustain airbag system reliability. You implement maintenance intervals aligned with manufacturer guidance, industry standards, and vehicle usage patterns. Establish baseline inspections for connector corrosion, terminal cleanliness, and seal integrity at each service milestone. Your maintenance schedules should specify visual checks, electrical tests, and connector torque verification, with documented pass/fail criteria. Prioritize proactive preventive steps: replace damaged seals, re-torque fasteners to spec, and clean connectors with approved contact cleaners only. Schedule more frequent checks for high-humidity environments, frequent exposure to road salt, or older harnesses, and record any corrective actions taken. Documentation practices require dated entries, technician initials, diagnostic results, and component part numbers. Maintain a centralized log accessible to service teams and, when appropriate, the customer. Regular audits of records guarantee traceability, accountability, and continual improvement of airbag connector reliability.
Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting Tips
Be aware of connector corrosion signs, as degraded connections can mimic failure indicators and compromise system integrity. Consider moisture intrusion risks that can accelerate corrosion or sensor shorting, and address sealing or enclosure breaches promptly. If a fault is suspected, follow prescribed troubleshooting steps for failure in a documented, stepwise sequence to confirm diagnosis and determine corrective actions.
Connector Corrosion Signs
Corrosion at the airbag connector is a common, solvable fault that can undermine signal integrity or trigger failure warnings. You should identify signs early to prevent sudden fault codes, misreads, or degraded harness performance. Look for diffuse or blooming discoloration on contact surfaces, flaky oxidation on pins, and dark residue that indicates ionic activity. Visual checks alone aren’t sufficient; perform a gentle resistance test across the connector pair to detect increased contact impedance. Document any pin deformation, looseness, or uneven mating surfaces, which reveal wear in connector types. Corrosion causes often stem from poor material compatibility, inadequate sealing, or environmental exposure. Address symptoms by cleaning with approved contact cleaner, reseating, and replacing severely degraded components promptly to maintain reliable communication and system integrity.
Moisture Intrusion Risks
Moisture intrusion poses a primary risk to airbag systems, often causing intermittent faults, false warnings, or degraded sensor signals. You should map potential moisture sources around connectors, housings, and seals, then verify seals meet spec and installation torque. Establish a clean-room mindset during inspection to prevent contamination that accelerates corrosion. Identify rain, humidity, storage condensation, and wash-water ingress as primary vectors, and implement targeted moisture control: desiccant use in storage, sealed enclosures, and proper ventilation where needed. Prioritize corrosion prevention by inspecting gaskets, terminal coatings, and connector housings for micro-cracks and corrosion pits. Document exposure events, remediation steps, and preventive actions, then revisit after service. Maintain traceable records to support long-term reliability and consistent performance.
Troubleshooting Steps for Failure
When failures occur in airbag systems, a structured troubleshooting approach helps isolate the issue quickly and safely. You should begin with a clear problem statement, confirm fault codes, and reference service manuals for diagnostic flow. Next, verify power, grounding, and enable/disable states, then inspect connectors for corrosion detection and signs of moisture ingress. If corrosion or oxidation is present, perform targeted cleaning and, where allowed, apply corrosion-inhibiting compounds; otherwise, replace compromised components to restore reliability. Document every step, test results, and recheck after repairs. Maintain strict safety practices and use calibrated tools. Emphasize preventative connector maintenance to prevent recurrence. Finally, revalidate system functionality with a controlled test, ensuring no intermittent faults linger and the airbag subsystem remains compliant with standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should I Replace Airbag Connectors as a Preventive Measure?
You should replace airbag connectors on a strict schedule, typically every 5 to 7 years, or sooner if you notice corrosion or moisture ingress. This aligns with standard maintenance frequency for critical safety components. Monitor connector lifespan through regular inspections, looking for corrosion, looseness, or damaged seals. If any defect is found, replace immediately and document the maintenance. Maintain a precise log; your maintenance frequency should reflect environmental exposure and usage to preserve reliability.
Can Aftermarket Cleaners Be Used on Airbag Connectors Safely?
Yes, you should avoid aftermarket cleaners on airbag connectors due to safety concerns. They can leave residues or cause corrosion that impacts connector safety. If you must clean, use manufacturer-approved products and follow prescribed procedures, applying minimal moisture and avoiding contact with the airbag module. Inspect connectors for damage afterward. Regular inspection and professional servicing are essential; never improvise. Prioritize connector safety and documented, standards-driven methods to protect your system.
Does Weather Exposure Affect ABS Connector Longevity Differently Than Airbags?
Weather can wear ABS connectors differently, but both endure environmental stress. Yes, exposure tends to affect ABS durability and Airbag lifespan, though atmospherics may hit ABS circuits with more rapid abrasion than airbags. You should treat connectors with care, document environmental factors, and follow standards-driven inspection intervals. You’ll value precise maintenance, measuring corrosion risk, ensuring sealed enclosures, and using appropriate conductive coatings. In freedom’s scope, monitor wear, uphold safety, and preserve system integrity.
Are There Warning Signs Before Connector Corrosion Becomes Critical?
Warning signs exist before connector corrosion becomes critical. You’ll notice intermittent airbag or ABS warnings, dim or flickering dashboard indicators, or physical corrosion at terminals. Conduct a systematic inspection for overheating, melted insulation, loose fittings, or greenish/or white crust. If you detect any warning signs, de-energize, clean with approved contact cleaner, reseat connectors, and replace affected parts promptly. Maintain documentation and follow standards to prevent escalation, prioritizing safety, reliability, and freedom to drive with confidence.
What Are Legal Implications of Servicing Airbag Systems at Home?
Answering directly: servicing airbag systems at home carries significant legal liability and often violates DIY regulations. You might face fines, voided warranties, or civil liability if a fault causes injury. Juxtaposed with safety-minded precision, you should instead rely on certified technicians who follow standards-driven protocols. You retain freedom by choosing compliant paths, documenting work, and avoiding unauthorized repairs. In short, don’t DIY airbags; consult licensed pros to minimize legal risk and maximize safety.