When a Rebuild Is Necessary for Gearbox Bearings
A rebuild for gearbox bearings is necessary when you notice increased noise, excessive vibrations, or significant temperature rises, all indicating wear or potential failure. If you observe lubricant contamination or reduced performance efficiency, it’s time to act. Regular inspections will help catch these issues before they escalate. Don’t ignore signs like grinding noises or unusual heat buildup; they can lead to serious problems. There’s more to understand about ensuring ideal performance and longevity of your gearbox components.
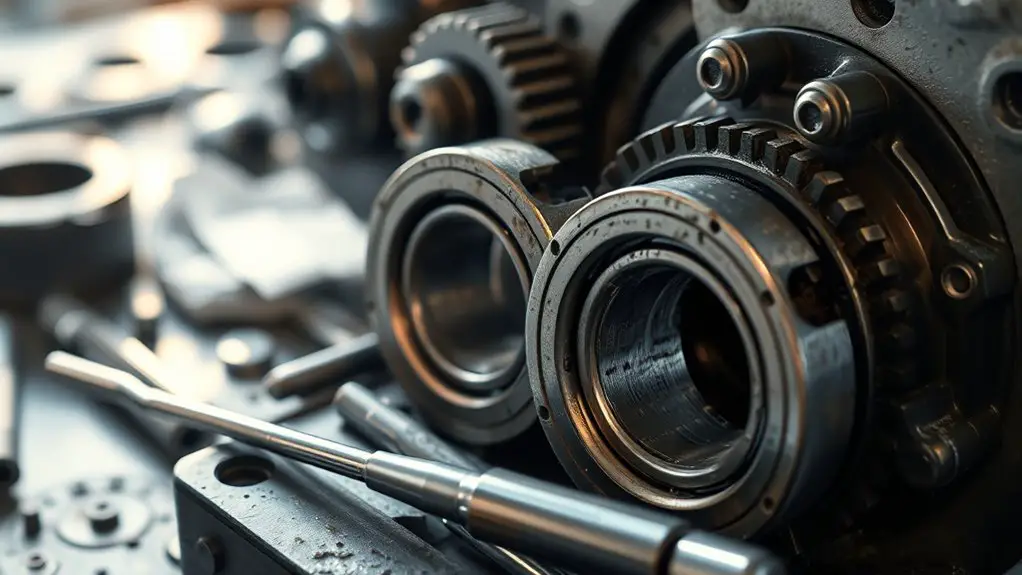
Common Signs of Gearbox Bearing Wear

When you’re operating machinery that relies on gearbox bearings, it’s crucial to recognize the common signs of wear that can indicate impending failure. One of the first indicators is increased noise, such as grinding or whirring, which often suggests improper alignment or deterioration. You’ll also want to monitor vibrations; excessive or irregular vibrations can signal bearing degradation. Additionally, inspect for heat buildup—if the bearings are running hotter than normal, it’s a red flag for potential issues.
Another key aspect is lubricant contamination, which can lead to bearing failure if not addressed. Regularly reviewing maintenance schedules can help catch these signs early, preventing costly repairs. Pay attention to any changes in performance or efficiency, as these can also indicate that your bearings are nearing the end of their operational life. By staying vigilant, you can guarantee your machinery remains reliable and efficient.
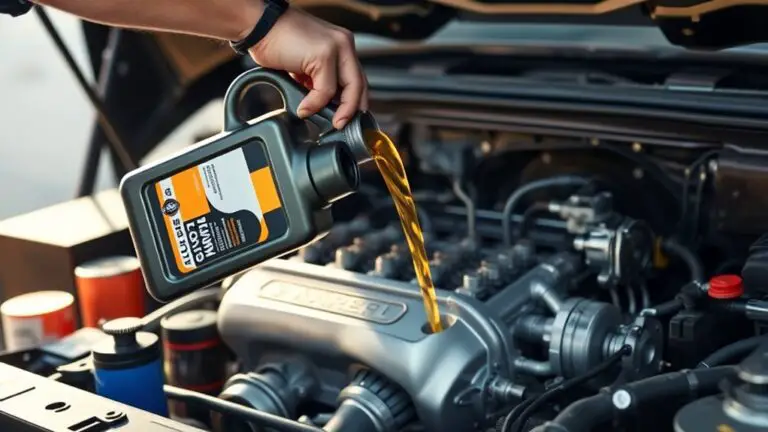
The Impact of Improper Lubrication

Although lubrication is often seen as a minor detail, improper lubrication can have severe consequences on gearbox bearings. You might think that any lubrication type will suffice, but choosing the wrong one or applying it incorrectly can lead to premature wear, overheating, and ultimately, failure. It’s critical to adhere to the recommended maintenance schedules for your gearbox, as this guarantees ideal performance and extends lifespan.
Inadequate or excessive lubrication can create a hostile environment, leading to contamination or ineffective heat dissipation. Different lubrication types serve distinct purposes, and understanding these can help you make informed choices. For instance, synthetic oils may offer better protection in high-stress conditions compared to conventional oils. By prioritizing proper lubrication practices, you not only safeguard your gearbox bearings but also enhance overall operational efficiency, granting you the freedom to pursue your tasks without the looming threat of unexpected downtime.
Identifying Unusual Noises and Vibrations
Improper lubrication can lead to more than just wear and tear; it can also manifest in unusual noises and vibrations from the gearbox. Identifying these irregularities is essential for effective noise diagnostics and vibration analysis. You need to be attentive to the sounds and vibrations your gearbox produces.
| Noise Type | Potential Cause | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Grinding noise | Worn bearings | Inspect and replace |
| High-pitched whine | Misalignment | Realign components |
| Thumping | Loose parts | Tighten or replace |
| Constant rumble | Insufficient lubrication | Check oil levels, lubricate |
Evaluating Temperature Increases
When evaluating temperature increases in gearbox bearings, it’s vital to understand the underlying causes such as lubrication failure or misalignment. You’ll also want to implement effective monitoring techniques to track temperature variations over time. Recognizing these factors is important, as excessive heat can notably impact performance and lead to premature failure.
Causes of Temperature Rise
As you evaluate temperature increases in gearbox bearings, it is vital to recognize that several factors can contribute to a rise in temperature. One primary cause is heat generation due to friction between moving parts. Insufficient lubrication can exacerbate this issue, leading to increased wear and further heat production. Additionally, thermal expansion of materials can result in tighter fits, restricting movement and causing additional friction. Operating conditions, such as load and speed, also play a significant role; higher loads can increase stress on bearings, resulting in elevated temperatures. Finally, environmental factors like ambient temperature and airflow can affect cooling efficiency. Understanding these causes is important for diagnosing issues and ensuring the longevity of gearbox bearings.
Monitoring Techniques Overview
Effective monitoring techniques are essential for evaluating temperature increases in gearbox bearings, especially after identifying potential causes of temperature rise. By employing advanced monitoring technologies, you can guarantee peak performance and longevity of your equipment. Implementing predictive maintenance strategies allows you to address issues before they escalate.
- Utilize infrared thermography to identify hot spots quickly.
- Integrate vibration analysis to detect abnormal patterns correlating with temperature spikes.
- Employ continuous temperature monitoring systems for real-time data collection.
These methods not only enhance your understanding of temperature dynamics but also empower you to make informed decisions, ultimately leading to improved maintenance practices and reduced downtime. Embrace these techniques for a more reliable and efficient operation.
Impact on Performance
Although temperature increases in gearbox bearings may seem minor, they can greatly impact overall performance and longevity. Elevated temperatures can lead to changes in material properties, resulting in decreased lubrication effectiveness and increased wear. This degradation affects critical performance metrics, such as load capacity and operational efficiency. You may find that your system struggles to meet established efficiency benchmarks, causing not only a drop in performance but also potential failures that could necessitate costly repairs. Monitoring temperature trends is crucial; addressing issues early can help you maintain ideal performance and extend the lifespan of your gearbox. By prioritizing temperature evaluation, you’re enhancing reliability and ensuring that you meet the demands of your operational environment effectively.
Understanding Load and Stress Factors
Understanding load and stress factors is essential for guaranteeing the longevity and reliability of gearbox bearings. By analyzing how load distribution affects performance, you can identify potential issues before they escalate. Conducting a thorough stress analysis allows you to pinpoint areas where excessive forces might lead to premature wear or failure.
- Evaluate the load distribution to guarantee even weight across bearings.
- Monitor stress factors that could compromise structural integrity.
- Implement corrective measures to alleviate stress concentrations.
The Importance of Regular Inspections
Regular inspections are vital for maintaining gearbox bearings, as they help identify potential issues before they develop into significant failures. By employing various inspection techniques, you can monitor the condition of the bearings and guarantee peak performance. The inspection frequency should be tailored to the specific operating conditions, yet regular checks are essential.
Here’s a quick overview of common inspection techniques:
| Inspection Technique | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Detects surface damage |
| Vibration Analysis | Identifies misalignment |
| Temperature Monitoring | Assesses overheating |
| Oil Analysis | Reveals contamination |
| Ultrasonic Testing | Detects internal flaws |
Incorporating these techniques into your maintenance routine empowers you to act proactively, ultimately prolonging the lifespan of your gearbox bearings. Regular inspections not only enhance reliability but also minimize unplanned downtime, giving you greater freedom in your operations.
Steps to Effectively Rebuild Gearbox Bearings
After identifying potential issues through thorough inspections, the next step is effectively rebuilding gearbox bearings to restore their functionality. Utilizing proper rebuild techniques is essential during this process to guarantee longevity and performance. Begin by disassembling the gearbox carefully, documenting each step for reference. Inspect all components for wear and tear, and proceed with bearing replacement as necessary.
Consider these key points:
- Cleanliness: Maintain a clean workspace to prevent contamination during assembly.
- Alignment: Ensure proper alignment of the bearings to minimize friction and wear.
- Lubrication: Use the appropriate lubricant to reduce heat and enhance efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Do Gearbox Bearings Typically Last?
Gearbox bearings typically last between 10,000 to 20,000 hours, akin to a steadfast ship riding the waves. However, their lifespan’s greatly influenced by your maintenance habits. Regular lubrication and monitoring for wear can extend their journey, ensuring they don’t falter when you need them most. To truly embrace freedom in your machinery, stay vigilant with maintenance tips, and your bearings will sail smoothly through the storms of wear and tear ahead.
Can I Replace Just One Bearing in a Gearbox?
You can replace just one bearing in a gearbox, but it’s essential to guarantee bearing compatibility with the existing components. Replacing only one may lead to imbalances or premature failure if the new bearing doesn’t match the others. For effective gearbox maintenance, consider inspecting all bearings to assess their condition. This approach helps maintain overall performance and longevity, allowing you the freedom to operate your machinery efficiently without unnecessary downtime.
What Tools Are Needed for a Gearbox Rebuild?
To tackle a gearbox rebuild, you’ll need essential gearbox tools that serve as your trusted allies. Start with a torque wrench for precise measurements, a bearing puller for easy removal, and a set of sockets for disassembly. Don’t forget a sealant for leaks and a dial gauge to check alignment during the rebuild process. With these tools in hand, you’re well-equipped to restore functionality and reclaim your gearbox’s performance.
How Much Does It Cost to Rebuild Gearbox Bearings?
Rebuilding gearbox bearings typically costs between $500 and $2,500, depending on the gearbox type and complexity. For effective gearbox maintenance, always assess the specific needs and potential issues before proceeding. Factors influencing rebuilding costs include labor rates, parts quality, and any additional repairs required. By understanding these aspects, you can make informed decisions that align with your desire for freedom in managing your machinery’s performance and reliability.
Is Professional Help Necessary for a Gearbox Rebuild?
“Don’t bite off more than you can chew.” When tackling a gearbox rebuild, professional help’s often necessary due to gearbox complexity. Without sufficient repair experience, you might overlook critical issues or misassemble components, leading to further damage. Experts possess the specialized knowledge and tools to guarantee a precise rebuild, safeguarding your equipment’s functionality. Relying on professionals allows you the freedom to pursue other projects while guaranteeing your gearbox operates effectively and efficiently.







