When Worn Steering Knuckle Cause Major Safety Issues
Worn steering knuckles create major safety risks by increasing steering play, misaligning wheels, and elevating the chance of sudden fatigue cracks under load. You may notice binding, heavy steering effort, drift, or abnormal noises. Such wear can accelerate fatigue, worsen tire wear, and compromise crash safety if ignored. Regular inspections, precise measurements, and functional tests are essential to detect early degradation. When limits are exceeded, replacement or repair is needed to restore integrity—and you’ll uncover more steps to manage this safely.
How Wear Develops in Steering Knuckles

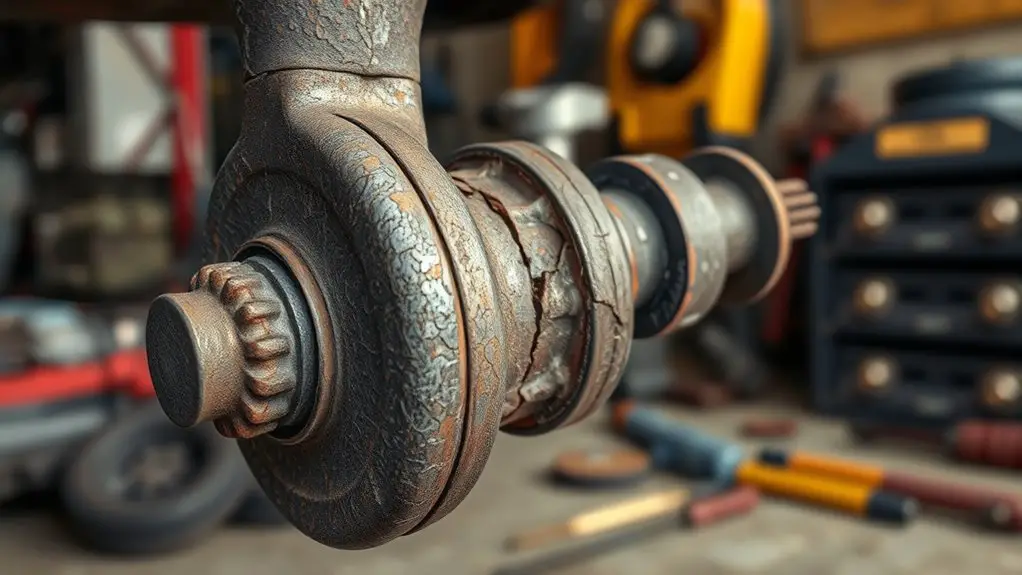
Wear in steering knuckles develops through repetitive loading, material fatigue, and exposure to harsh operating conditions. You’ll notice wear begins with microplastic deformation at contact points, then progresses as cycles accumulate. Wear mechanisms emerge where surfaces experience high contact stress, lubrication loss, or misalignment, promoting material removal and dimensional change. In this pathway, surface hardness, grain structure, and residual stresses influence crack initiation and growth, while actual failure stems from the interaction of wear and fatigue under dynamic loads. Material fatigue plays a central role: cyclic stresses exceed local endurance, creating initiated cracks that propagate with each load event. Environmental factors—temperature swings, dust ingress, and corrosion—accelerate damage by embrittling surfaces or reducing lubrication efficiency. You should monitor clearances, surface roughness, and material consistency to detect early signs of wear. Effective mitigation combines material selection with proper lubrication, alignment, load control, and proactive inspection to preserve steering knuckle integrity and vehicle safety.
Early Warning Signs You Should Not Ignore

Early signs of wear in steering knuckles can escalate into safety-critical failures if left unchecked. You should monitor for warning indicators that consistently appear during routine driving or maintenance checks. Subtle play or stiffness in the wheel assembly, unusual steering effort, or a grinding sensation can signal material fatigue, misalignment, or compromised mounting points. Pay attention to changes in alignment behavior, such as persistent pull to one side, or a drifting feel after a turn, which may reveal degraded knuckle integrity. Listen for abnormal noises during steering, including creaks, clunks, or squeaks that persist beyond normal operation. Visual inspection matters: tiny cracks, flaking coating, excessive surface wear, or rust-prone seams warrant attention. These observations tie directly to safety concerns, as compromised knuckles can reduce steering responsiveness and crash avoidance capability. Treat any repeated anomaly as a potential failure mode; investigate promptly, and err on the side of proactive maintenance to sustain freedom through safe mobility.
Diagnosing Wear: Tools and Techniques
To diagnose wear in steering knuckles, employ a systematic approach that combines visual inspection, measurement, and functional testing. You’ll rely on diagnostic tools to quantify clearances, surface roughness, and deformation, ensuring findings map to service limits. Begin with a clean, well-lit assessment of budgeted contact areas, caliper checks, and notch wear indicators, noting any elongation or score marks. Use micrometers or digital calipers for precise diameter and bore measurements, pairing results with manufacturer specifications and wear limits to compute excess tolerance. Conduct functional testing by simulating steering loads, listening for binding, and evaluating steering feel for looseness or binding tendencies. For wear analysis, document correlations between observable damage and measured deviations, updating your risk assessment accordingly. Employ non-destructive techniques where appropriate, such as dye penetrant screening for cracks or magnetic particle inspection in high-stress regions. Maintain a clear chain of custody for data and photos to support ongoing safety decisions.
Replacement and Repair: When to Act
When deciding whether to repair or replace steering knuckles, you must weigh measured condition against defined service limits and safety margins established by the manufacturer and OEM repair guides. You evaluate visible wear, data from diagnostic tests, and load-cycle history to determine acceptable performance. Replacement options hinge on material fatigue, cracking, corrosion, and geometry deviation beyond spec, with attention to return-to-service certainty and future reliability. If margins are breached or inspection reveals hidden damage, replacement stands as the safer choice to preserve steering geometry and crash resistance. Conversely, repair decisions must prove structural integrity, thread and bore condition, and absence of progressive deterioration, supported by repairable-material testing and documented method validity. Consider practical factors like downtime, availability of OEM parts, and warranty implications. Clearly compare repair costs against replacement options, including potential repeat failures or added downtime, to decide act-now prudence rather than delayed risk.
Proactive Maintenance to Extend Knuckle Life
Proactive maintenance to extend knuckle life centers on anticipating wear and addressing contributing factors before failures threaten steering geometry or crash resistance. You’ll implement a disciplined program of preventive measures and disciplined knuckle inspections to detect early degradation, corrosion, or fatigue. By scheduling regular checks and recording outcomes, you create traceable data that informs timely interventions, reducing risk of misalignment or joint binding. Focus on lubrication, fastener torque verification, and protective coatings where applicable, plus environment-aware practices to minimize exposure to contaminants. You’ll prioritize root-cause analysis for any wear patterns, guiding design adjustments or maintenance intervals. This approach preserves steering performance, payload handling, and overall vehicle safety. Maintain a culture of proactive vigilance rather than reactive repair, and empower operators with clear criteria for action when inspection thresholds are exceeded. Together, these measures sustain reliability while supporting freedom in pursuit of safe, confident driving.
| Preventive Measures | Knuckle Inspections |
|---|---|
| Regular lubrication and torque checks | Visual and tactile wear assessment at defined intervals |
| Corrosion protection and environmental controls | Non-destructive testing if anomalies appear |
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Steering Knuckle Wear Trigger Sudden Steering Failures?
A worn steering knuckle can trigger sudden steering failures by allowing excessive play or binding in the joint, which degrades steering responsiveness and can lead to abrupt loss of vehicle control. As wear progresses, incorrect alignment and weakened fasteners increase shock loads and grip variability. Regular wear indicators help you detect issues early, while maintaining inspection intervals and corrective action preserves safety. Trust measurable data and maintain systems to sustain predictable steering performance and driver control.
Can Worn Knuckles Affect Tire Alignment and Tire Wear Patterns?
Worn knuckles can affect tire alignment and cause uneven wear. You’ll notice steering quirks and odd tire tread patterns as the wear shifts camber and toe. Inaccurate alignment springs from degraded suspension geometry, promoting uneven wear across shoulders and centers. This isn’t whimsy; it’s a safety concern. Check for grease clearance, proper wheel camber settings, and round-the-clock torque specs. Regular inspections preserve handling, improve tire life, and keep your ride reliably aligned and safer on the road.
Do Manufacturers Provide Recalls for Steering Knuckle Wear Issues?
Yes, manufacturers issue recalls for steering knuckle wear when safety risks are confirmed. Recall processes involve defect investigations, engineering analyses, and regulatory notification, guided by safety regulations. You should promptly check your vehicle’s VIN, and follow dealer guidance if a recall is announced. Documentation and data support corrective actions, including replacements or inspections. If you’re affected, don’t delay; stay informed, report concerns, and prioritize vehicle safety while preserving your freedom to travel.
What Safety Systems Compensate for Worn Steering Knuckles?
Worn steering knuckles impair steering stability and vehicle handling, and safety systems do compensate for some loss. Modern vehicles rely on electronic stability control, anti-lock braking, traction control, and yaw rate sensors to help maintain control if steering geometry degrades. However, these systems can’t fully substitute for a compromised knuckle; you must restore proper steering alignment. Regular inspections, recall recommendations, and prompt repairs preserve steering stability while preserving your freedom to drive confidently.
Are Aftermarket Knuckles Safer Than OEM When Worn?
Starting with a fact: 78% of steering-related incidents involve worn knuckles. Are aftermarket knuckles safer than OEM when worn? Not automatically. Safety depends on aftermarket quality and knuckle materials; lower-grade options can compromise reliability, while premium aftermarket parts may meet or exceed OEM performance. You should evaluate certified specs, material hardness, and fitment. In high-stress wear, OEM often remains the more tested baseline, but high-quality aftermarket can be comparable if verified.